& Construction

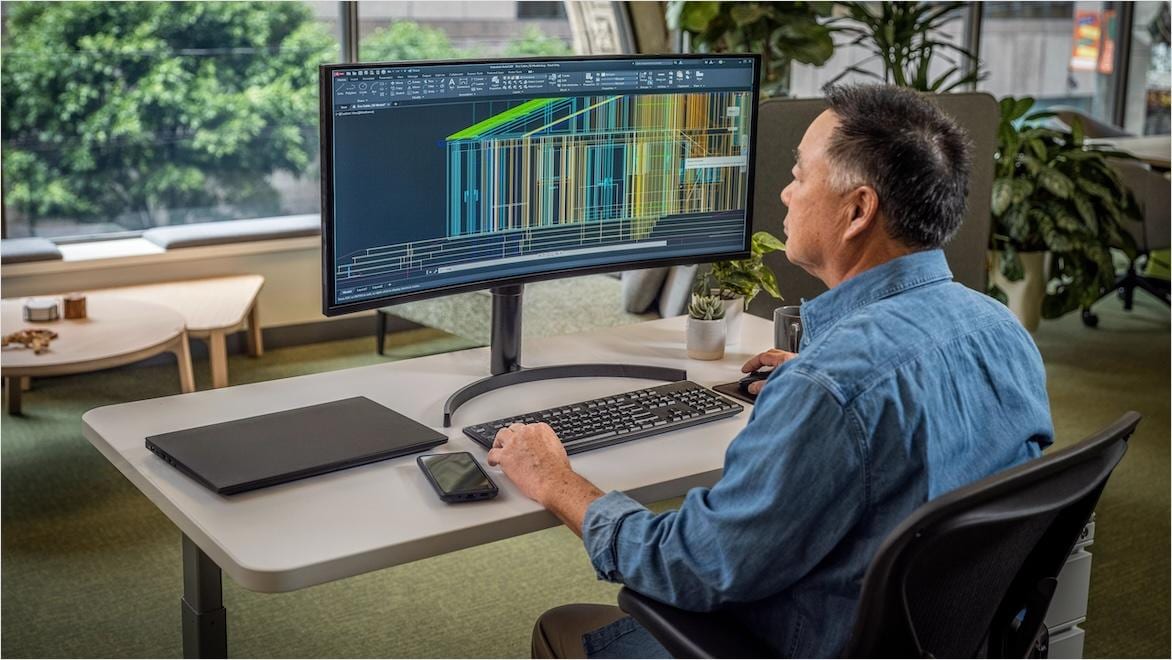
Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

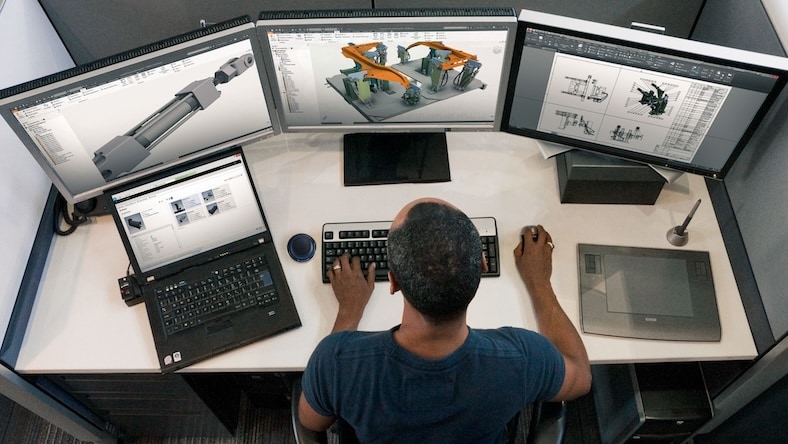
Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
CAD data exchange involves the process of transferring design information between CAD and non-CAD software applications. As a noun, it can also refer to a platform that facilitates the process.
The process of CAD data exchange is transforming the engineering and architecture industries by ensuring data interoperability, enhancing collaboration, and helping streamline the design-to-manufacturing process.
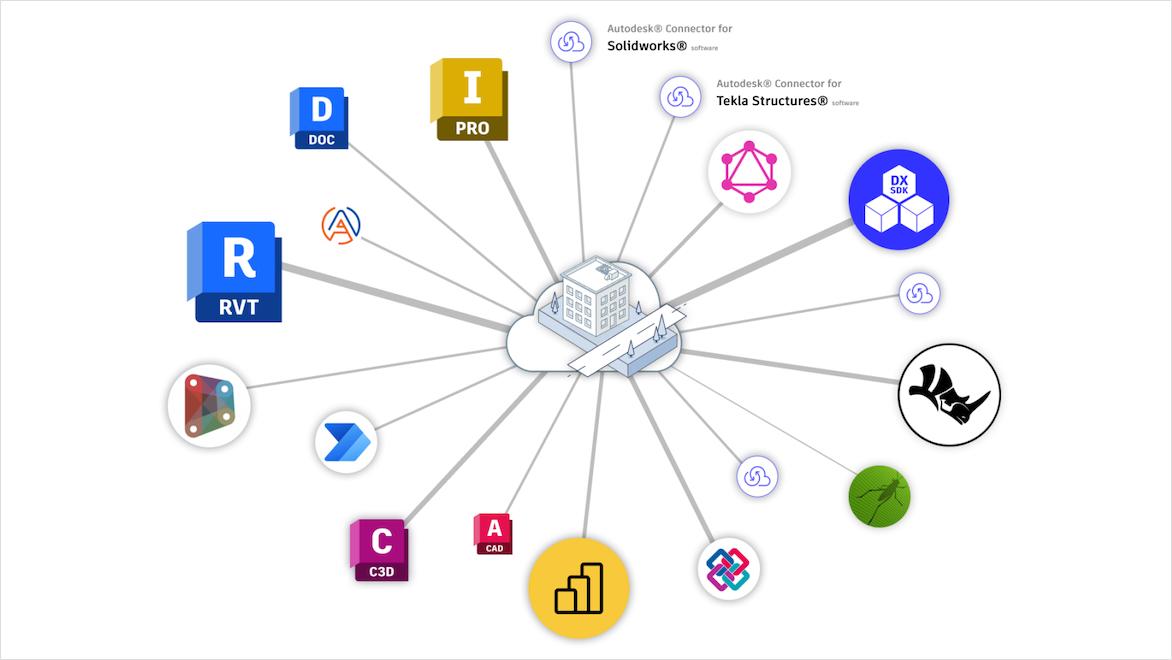
Interoperability is critical in today’s diverse design environments, allowing different CAD software systems to communicate effectively and more accurately transfer design information. Autodesk Data Exchange empowers collaborators to share and work with design & make data across teams and apps. Partners can work with more precise subsets of data they need instead of entire models. This eliminates the barriers posed by proprietary file formats so professionals can use various tools and platforms without losing essential data.
The CAD data exchange process fosters effective collaboration by allowing team members from different disciplines and locations to access and modify the same design files. Using standardized file formats like STEP and IGES reduces the risk of errors and miscommunication, creating a more cohesive and productive working environment. By ensuring more accurate data transfer from design to manufacturing, 3D CAD data exchange software helps streamline production processes, reducing lead times and minimizing errors, ultimately enhancing efficiency and lowering costs throughout the development cycle.
Navigating CAD data exchange challenges is essential for success in engineering and architecture. Critical areas include handling file format compatibility, ensuring more accurate data transfers, and adhering to specific tolerances and parameters.
Different CAD systems often use proprietary formats, leading to data loss or misinterpretation. Utilizing standardized formats like STEP, IGES, and STL, along with robust translation tools, ensures data consistency and usability across platforms.
It is crucial to maintain data integrity during transfers. Using advanced translation software to handle complex geometries and regularly validating transferred data against original designs helps maintain high standards of quality and precision.
Design often requires the preservation of specific tolerances and parameters. Implementing more precise translation protocols and strict validation criteria ensures these critical aspects are maintained, reducing the risk of costly errors and revisions.
Software and applications built using the process of CAD data exchange offer advantages that enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of engineering and architectural projects. Top benefits include:
CAD data exchange enables seamless sharing and modification of design files across teams, reducing errors and improving productivity.
Application programming interfaces (APIs) enable CAD data exchange workflows that support more accurate data transfer across different CAD and non-CAD software, including building information modeling (BIM) platforms, breaking down barriers posed by proprietary formats.
With the ability to retrieve just the components of data you need with granular data access designers no longer need to transfer big, bulky files with CAD data exchange.
CAD data exchange software and applications automate data transfer, saving time and resources and lowering overall project costs.
2D and 3D CAD tools, with enhanced insights, AI-automations, and collaboration features. Subscription includes AutoCAD on desktop, web, mobile, and seven specialized toolsets.
Powerful BIM and CAD tools for designers, engineers, and contractors, including Revit, AutoCAD, Civil 3D, Forma Site Design, and more
LMN ARCHITECTS
Discover how an architecture and urban design firm uses Autodesk Data Exchange API to create a dashboard-based solution that provides real-time control of model data.
CCTECH
Learn how one software company uses Autodesk Data Exchange SDK to create a connector that pulls live 3D model data directly into PowerPoint.
STANTEC
A global design consultancy uses the Autodesk Data Exchange API to enable two-way data sharing and reduce time spent on low-value tasks.
Learn about AutoCAD Connector 2024’s latest features and capabilities and exchange data between Autodesk and non-Autodesk applications.
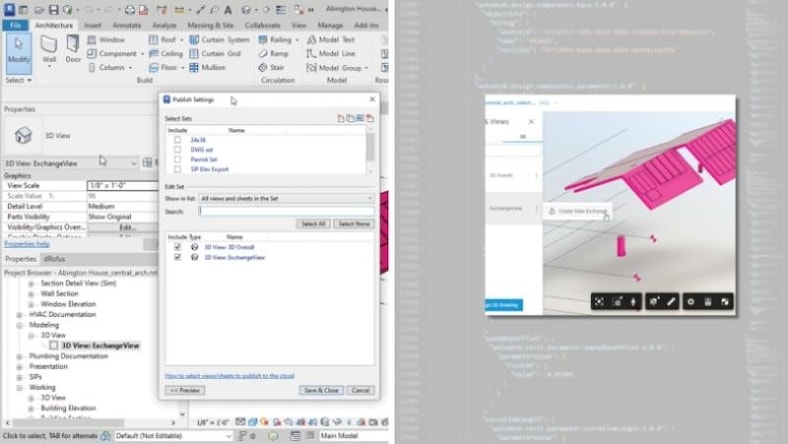
Explore the Autodesk Data Exchange API and share complete or selective 3D model data across BIM, CAD, and other applications.
Dive into the latest updates, code samples, announcements, and events from Autodesk Platform Services.
CAD data exchange is the process of transferring design information between different CAD and non-CAD software applications or systems. This process ensures that geometric and non-geometric data, like dimensions, tolerances, materials, and annotations, can be shared and interpreted more accurately across various platforms. By enabling data interoperability, CAD data exchange allows engineers, architects, and other stakeholders to collaborate effectively, help streamline workflows, and maintain data integrity throughout the design and manufacturing process.
Partners can work with more precise subsets of data they need instead of entire models.
CAD data exchange involves three primary types:
These methods ensure a more accurate and efficient transfer of design information across platforms.
CAD data is stored in digital files that capture geometric and non-geometric design information. Geometric data includes 3D shapes, 2D drawings, and dimensions, while non-geometric data encompasses material properties, tolerances, and annotations. This data is stored in various file formats, either proprietary (e.g., .dwg, .prt, .sldprt) or neutral (e.g., STEP, IGES, STL), and can also be managed in databases within product data management (PDM) or product lifecycle management (PLM) systems. Increasingly, CAD data is stored in the cloud, facilitating easier access, collaboration, and backup. This comprehensive approach ensures more accurate and accessible design information for architecture and engineering.