& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
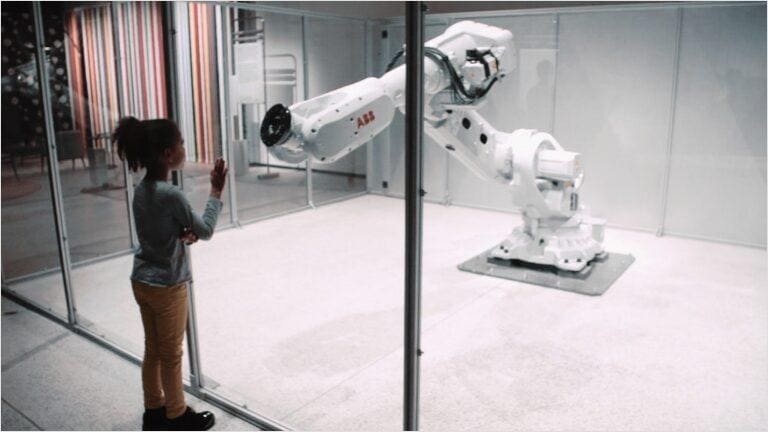
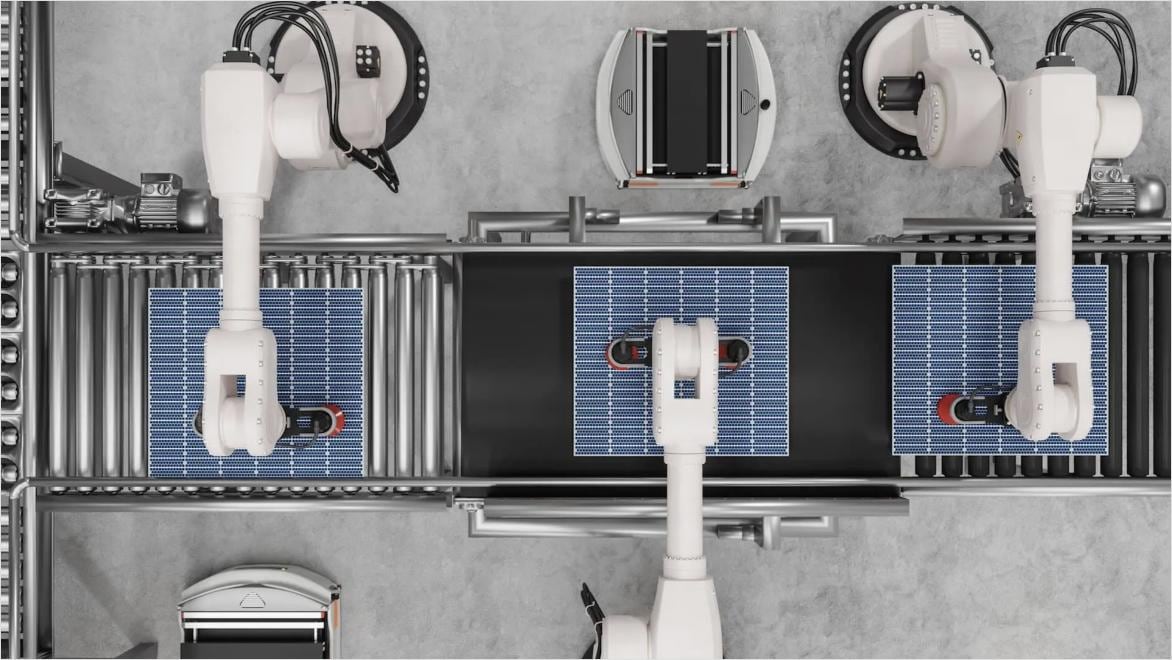
A cobot, short for collaborative robot, is a robotic system designed to work alongside human workers in a shared workspace.
Unlike traditional robots, cobots are built with safety features, such as sensors, to interact directly with humans, offering a safe and efficient collaboration. Cobots are typically lightweight, flexible, and adaptable, making them ideal for tasks that require precision or repetitive motions. These robots enhance human capabilities, often taking over mundane, high-precision, or physically demanding tasks, allowing workers to focus on more complex, creative work.
Cobotics refers to the field of technology and engineering focused on enabling collaborative interaction between humans and robots. It merges robotics with human-centric design, emphasizing shared tasks, mutual responsiveness, and intelligent workflows.
Cobotics is driving a shift from automation to augmentation, where machines support and elevate human work rather than operate independently from it.
Cobots function through a combination of sensor inputs, control software, and machine learning algorithms. They are equipped with cameras, force sensors, and other devices that allow them to detect their surroundings, adapt to human interaction, and perform tasks with a high degree of safety.
Programming a cobot can be intuitive, often involving manual teaching (physically guiding the robot), drag-and-drop interfaces, or integration with CAM software like Autodesk Fusion.
There are several types of cobots, each suited for different tasks in the manufacturing process.
Equipped with sensors that detect human contact and stop automatically if the force exceeds safe limits.
These robots are manually controlled by human operators, teaching them tasks through physical interaction.
Using laser scanners, these cobots slow down or stop when a human enters their workspace and resume when the human moves away.
These robots stop completely when a human enters their workspace and only resume once the area is clear.
Understanding the key differences between cobots and traditional industrial robots helps determine the best fit for your manufacturing needs—balancing safety, flexibility, and efficiency.
High-speed machines for repetitive, high-volume tasks. Usually operate in isolation and need expert programming.
Collaborative robots built to safely work with humans. They’re flexible, easy to program, and ideal for adaptable, low-volume tasks.
Cobots are designed with sensors and force limitations, allowing them to work safely next to humans without the need for safety cages or barriers.
Unlike traditional robots, cobots can be installed and programmed quickly with intuitive software—reducing downtime and enabling rapid changes in workflows or tasks.
Cobots are lightweight and portable, making them easy to move between workstations. This flexibility is ideal for changing production needs or varied batch sizes.
Cobots handle repetitive or ergonomic tasks, freeing human workers to focus on higher-value work. The result is better efficiency and a more engaged workforce.
Cobots should work safely, intuitively, and flexibly alongside humans. Here are five core principles to keep in mind:
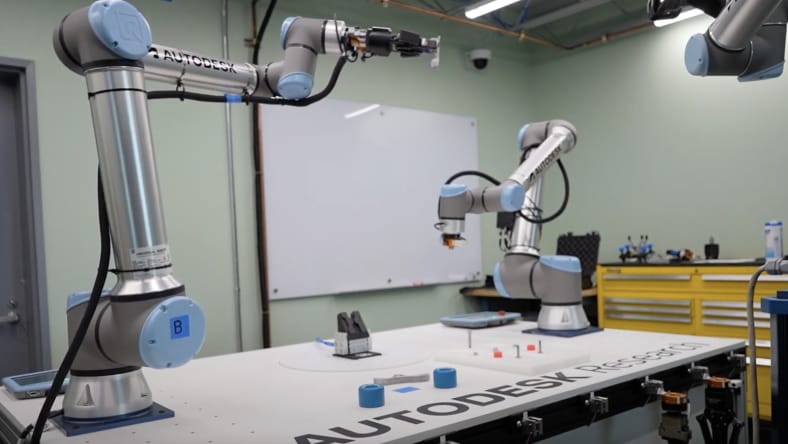
Autodesk Fusion offers powerful tools that make designing, testing, and optimizing cobots more efficient and accessible. Here are six essential features that support cobotic innovation:
Design teams can work together in real-time, streamlining feedback and updates across mechanical, electrical, and software components.
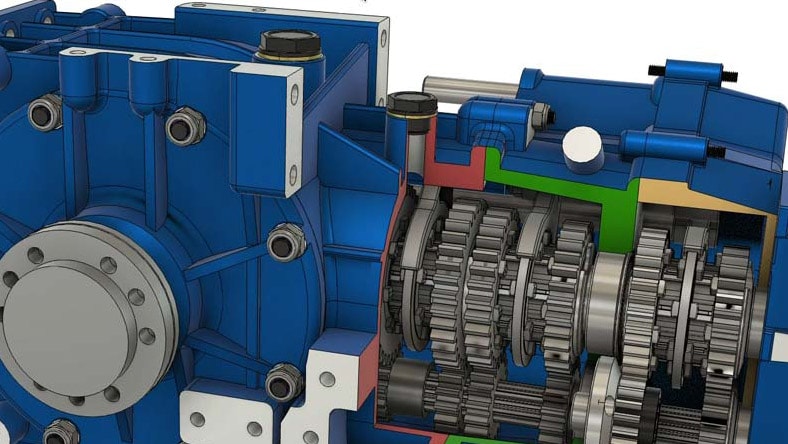
Quickly build and refine complex cobot geometries, custom joints, and end-effectors with parametric and free-form modeling tools.
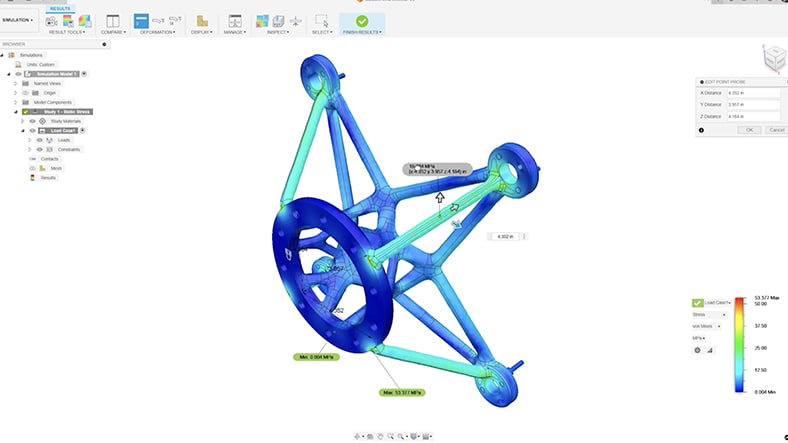
Validate how your cobot designs will perform under real-world conditions—test loads, motion, and stress before physical prototyping.
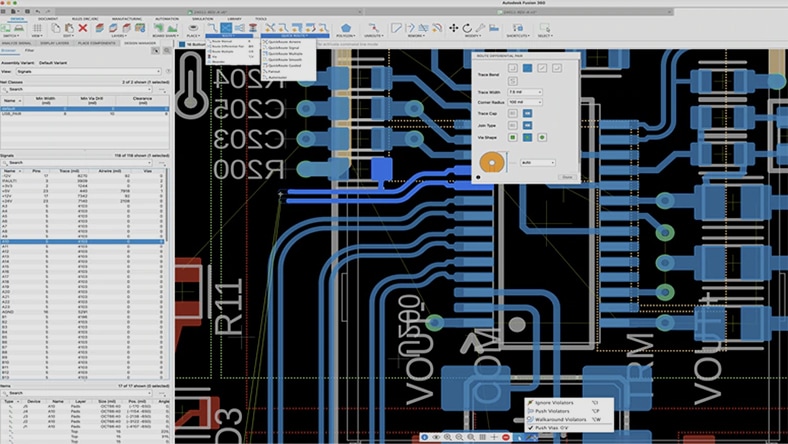
Design the electronic systems powering your cobots, including PCBs, directly within the same workspace as mechanical parts.
Automatically explore optimized structural forms for strength, weight, and material usage—ideal for cobot arms and structural frames.
Seamlessly connect design to CAM and CNC workflows, making it easier to machine parts and prototype rapidly with the Manufacturing Extension.
Discover how Fusion’s powerful CAD, CAM, data management, and collaboration tools streamline the design, programming, and manufacturing of collaborative robots for smarter automation.
Essential Design Tools
3D modeling for cobot components
Create custom grippers, mounts, sensors, and arms with versatile solid, surface, and mesh modeling tools.
Cloud-based collaboration
Enable seamless teamwork through real-time design sharing and multidisciplinary coordination.
Centralized data management
Securely store and access all your design, simulation, and manufacturing files in one place, simplifying maintenance and upgrades.
Integrated end-to-end workflow
Move effortlessly from design to manufacturing programming to simulation, speeding up cobot deployment across teams and stages.
Advanced Cobot Programming
Advanced CAM programming
Program cobots for complex milling, turning, and cutting tasks using precision CAM tools designed for modern manufacturing workflows.
Optimized toolpaths for efficiency
Cut cycle times and reduce energy use with intelligent toolpath strategies tailored to cobot operations.
Cobot simulation & verification
Virtually test cobot movements and interactions in a digital twin environment, eliminating costly errors before physical deployment.
Integrated quality control
Automate inspection tasks by programming quality workflows directly within Fusion, ensuring consistent product standards and less rework.
Scalable automated workflows
Confidently scale production by automating repetitive or complex cobot processes without sacrificing safety or performance.
As manufacturers face increasing pressure to improve efficiency, safety, and adaptability, cobots are becoming essential on the factory floor. These collaborative robots enhance workflows by working safely alongside humans, handling repetitive or precision tasks with ease.
When powered by Autodesk Fusion, cobotics goes beyond automation. Fusion’s cloud-based platform connects design and manufacturing in one place, making it easier to prototype, simulate, and optimize cobot components. Together, cobots and Fusion enable faster innovation, flexible production, and a smarter, more responsive approach to modern manufacturing.
Cobots become even more effective when paired with digital twins. These virtual models simulate real-world conditions, enabling teams to monitor performance, test improvements, and predict issues—before anything happens on the shop floor.
Benefits:
More accurate design validation and testing
Real-time performance monitoring and adjustments
Predictive maintenance planning to avoid costly failures
Digital twins will continue to close the gap between virtual design and physical performance, making cobots more adaptive and manufacturers more proactive.
IIoT connects cobots to smart devices and systems, creating a network of data that helps manufacturers monitor, control, and optimize production in real time.
Benefits:
IIoT will make cobots an essential part of responsive, self-correcting manufacturing ecosystems where machines can communicate, coordinate, and learn from one another.
Fusion empowers cobots with machine learning capabilities, enabling them to adapt to changing tasks, improve through repetition, and make smarter decisions based on data.
Benefits:
As ML becomes more sophisticated, cobots will take on more complex roles, continuously improving without the need for reprogramming—just data and design insights.
By analyzing past data and usage patterns, Fusion helps cobots anticipate maintenance needs and performance drops before they impact production. This keeps lines moving and cuts costs.
Benefits:
Predictive analytics will evolve into autonomous maintenance scheduling, where cobots alert teams—or even service themselves—before issues arise.
Learn how cobots and Autodesk Fusion transform manufacturing by boosting efficiency enhancing safety and accelerating innovation with smart automation.
Discover how artificial intelligence in manufacturing boosts efficiency, improves quality, and drives innovation with Autodesk Fusion’s AI-powered tools.
Explore how smart factories use AI, IoT, cobots, and automation to boost flexibility, efficiency, and customization in modern manufacturing.
Cobots improve factory operations by automating repetitive or dangerous tasks, reducing human error, and enhancing worker safety. They work alongside employees, allowing humans to focus on more complex and creative activities.
Autodesk Fusion supports this integration by providing powerful design and simulation tools that help engineers create, test, and optimize cobot workflows and components before implementation—saving time and costs while ensuring smooth and efficient factory automation.
Traditional industrial robots usually require safety cages or barriers because they operate at high speeds and forces, posing risks to humans nearby. Cobots, however, are built with sensors and safety protocols to detect and avoid collisions, enabling them to work side-by-side with people. Cobots are more flexible, easier to program, and designed for smaller-scale or variable tasks. This makes them suitable for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and diverse production environments.
No, cobots are user-friendly and easy to program. Many models feature intuitive interfaces, drag-and-drop programming, or teach-by-demonstration methods where operators physically guide the robot through a task sequence. This reduces the need for specialized programming skills, allowing even operators without extensive robotics experience to set up and modify cobot workflows quickly.
Cobots come equipped with multiple safety features, including:
The stages of product lifecycle management (PLM) typically include the following:
1. Concept and ideation: This stage encompasses idea generation, market research, and preliminary feasibility assessments. It involves brainstorming sessions, conceptual development, and the definition of the product's requirements and specifications.
2. Design and development: During this stage, detailed product designs are crafted using tools such as CAD (Computer-Aided Design). Prototypes are developed and tested, with iterative design adjustments made to enhance the product. This stage also involves conducting engineering analysis and validation.
3. Production and manufacturing: After finalizing the design, the product transitions into the production phase. This stage involves comprehensive planning, sourcing materials, executing manufacturing processes, assembly, and implementing quality control measures. It ensures the product is produced efficiently and adheres to quality standards.
4. Market launch: The product is introduced to the market during this stage. It involves marketing, sales, distribution, and customer support.
5. Growth: During the growth stage, the product gains market acceptance and demand increases. Efforts are made to optimize production, improve distribution, and enhance marketing campaigns to maximize sales.
6. Maturity: The product reaches peak market penetration in the maturity stage. Sales stabilize, and focus shifts to maintaining market share, optimizing operations, and extending the product's lifecycle through updates or enhancements.
7. Decline: The product enters the decline stage as market demand decreases, often due to technological advancements, changing customer preferences, or increased competition. Strategies are developed for product discontinuation, cost reduction, and transitioning customers to newer products.
8. Retirement:The final stage involves phasing out the product from the market. This includes managing inventory, providing support for existing customers, recycling or disposing of the product, and transitioning to new product offerings.
Cobots easily connect with legacy systems using common industrial protocols like Ethernet/IP and Modbus, ensuring smooth communication. They can be customized to work alongside older machines, often using middleware to bridge technologies. Autodesk Fusion’s simulation tools help engineers test and optimize these integrations virtually before deployment, reducing downtime and speeding up implementation.
Yes, standards like ISO/TS 15066 set safety requirements for cobots working alongside humans. Adhering to these ensures risk mitigation. Fusion’s design extensions help engineers validate safety features in their robotic components.
Cobots are used in various industries, including:
Their versatility makes them suitable across many sectors that require both flexibility and automation.
Yes, cobots can operate continuously and are often deployed for round-the-clock tasks, especially in environments that require repetitive or precise work. However, like all machinery, they require routine maintenance and occasional calibration. Operators typically schedule downtime for preventive maintenance to ensure consistent performance and avoid unexpected failures.
Cobots play a vital role in Industry 4.0 by integrating with IoT devices, data analytics, and AI-driven systems to create smart, connected manufacturing environments. They provide real-time data on production processes, collaborate dynamically with humans and other machines, and enable flexible manufacturing that can quickly adapt to changing demands. Cobots help achieve higher efficiency, quality, and customization, essential elements of smart factories.