& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Smart manufacturing is part of a pratical strategy for success.
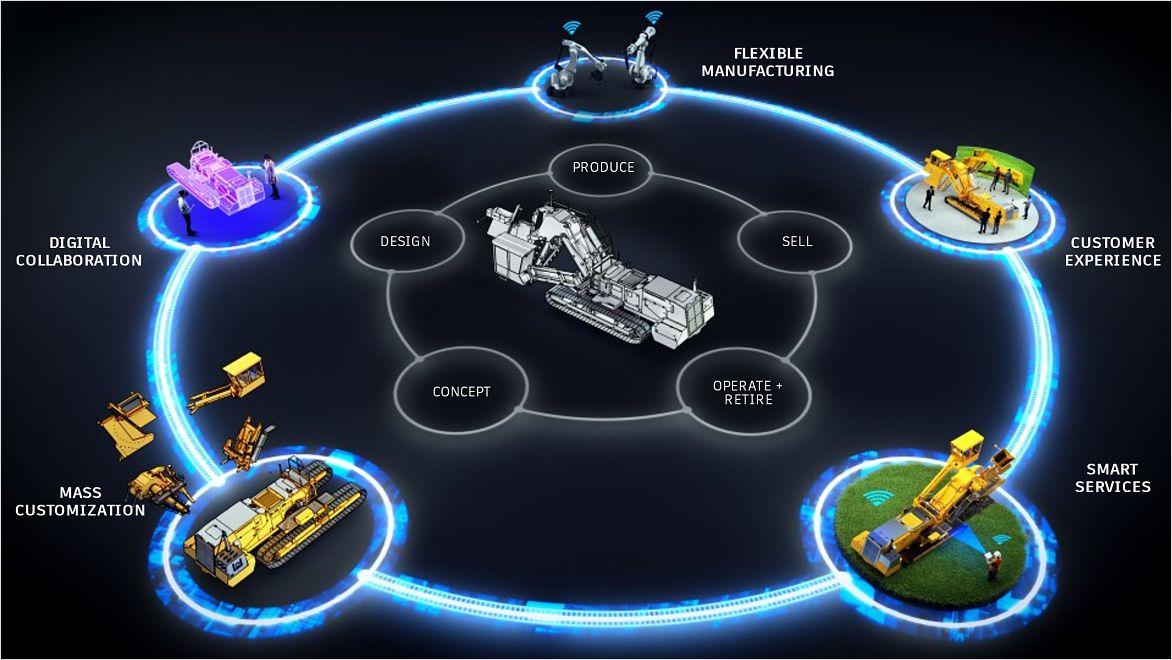
Smart manufacturing exemplifies the importance of digital transformation in the manufacturing industry. It represents a holistic integration of cutting-edge technologies across all facets of the manufacturing process, encompassing product design, supply chain management, production, distribution, and sales. Central to this transformation is the shift towards automation and robust data collection and analysis systems, which are fundamental in enhancing production efficiency and product quality. This modern approach starkly contrasts with traditional manufacturing methods, which often rely on less efficient and more rigid tools and systems.
In smart manufacturing, software acts as the linchpin, seamlessly connecting sensors, machinery, and systems across the production spectrum. This integration facilitates an extensive gathering and examination of data, forming a comprehensive technological ecosystem. This interconnectedness is instrumental in strengthening manufacturing efficiency, enabling companies to develop novel business models and practices. This evolution in manufacturing, driven by digital transformation, redefines efficiency standards and opens new horizons for creative and sustainable solutions in the industry.
Smart manufacturing software connects data and the physical world for real improvements in shipping, supply chain, quality control, and factory layouts.
Industry 4.0 and smart factories represent a transformative approach to manufacturing, where the connected ecosystem plays a pivotal role, demonstrated by tools like Autodesk's Fusion Industry Cloud.
At the heart of this process is the concept of a connected design and make environment. Tools like Autodesk's Fusion Industry Cloud enable designers and engineers to collaborate in real-time, breaking down traditional barriers between stages of product development. This integration facilitates a more fluid transition from design to manufacturing to production, where every aspect of the product lifecycle is interconnected and accessible.
In the realm of product creation, this means that designs are created and iteratively improved with direct input from the manufacturing process. Real-time feedback loops and simulations, powered by advanced software, allow for discrete event simulation. Every aspect of the product's creation is modeled and analyzed, from the materials used to the manufacturing techniques employed.
The focus shifts to the manufacturing process once the product design phase is complete. Here, the connected ecosystem shines, enabling factory throughput and optimization. Advanced software tools provide insights into the most efficient manufacturing processes, machine utilization, and workflow optimizations. This is where concepts like predictive maintenance come into play, but they are only one part of a larger picture. By continuously analyzing data from the factory floor, the system can identify bottlenecks, predict potential issues before they arise, and suggest improvements.
The result of this connected ecosystem is a smart factory that is agile, efficient, and capable of adapting to new challenges and opportunities. It's not just about maintaining machines but optimizing the entire production process, from the initial design phase to the final product being shipped. This holistic approach defines Industry 4.0, and tools like Autodesk's Fusion Industry Cloud are at the forefront of this transformation.
Smart manufacturing technologies, continually evolving, offer significant advantages even with partial adoption. Yet, fully embracing these technologies creates a continuous improvement cycle in operations. Key technologies include interconnected machines and systems, augmented reality for real-time insights, AI-driven predictive maintenance, and advanced data analytics for optimized decision-making.
AI/machine learning can process data and recognize patterns much faster than people. It may be embedded into smart factories’ robotics systems and cobots or in the microprocessors of edge computing IIoT devices in the form of computer vision or assembly line analysis.
Cloud computing with Big Data analysis significantly enhance decision-making in design and manufacturing. This technology offers deep insights for optimizing product design, streamlining manufacturing processes, improving quality control, and innovating production methods.
Robotics and CNC machinery offer immense value to companies that deploy them and are pivotal in smart manufacturing. These technologies automate complex tasks, enhance precision, and accelerate production, seamlessly integrating with Autodesk tools to optimize design-to-manufacturing workflows and drive innovation in a data-driven manufacturing landscape.
IIoT components, which include devices, machines, robots, or any objects with network-connected sensors, gather and upload data for analysis. Many of these sensors are edge computing devices equipped with low-cost processors to perform computing tasks locally. This local processing allows for initial data analysis or filtering at the source before the data is uploaded to the cloud, making them more efficient in data handling and transmission.
Extended reality (XR) encompasses augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) applications and hardware. These can include everything from smart manufacturing software like Autodesk VRED to Microsoft’s mixed-reality HoloLens 2 goggles. XR products have different smart manufacturing use cases, such as on-the-job training to help workers bridge the skills gap. XR is also useful for remote repairs, where a factory-floor employee receives instructions from a remote expert who essentially sees through the employee’s eyes.
Learn some of the top benefits of smart manufacturing software from Autodesk.
Maximize operational efficiency with advanced design and manufacturing tools that integrate seamlessly with IIoT sensors, providing real-time insights to optimize machine performance and product quality. Streamline training and bolster safety, all while gaining a competitive advantage in an industry where precision and smart innovation are key.
Enhance quality and reduce costs with integrated technologies that deliver real-time monitoring and data analytics, pinpointing inefficiencies and optimizing processes. Proactive quality control and self-diagnosing capabilities identify savings and elevate product standards, embodying the efficiency of a smart manufacturing ecosystem.
Some smart manufacturing software and technology uses are inherently resource-efficient. For example, simulation software reduces waste significantly by moving physical tests to a virtual space. Generative design software can reduce product weight and material used while maintaining strength. Smart manufacturing also streamlines operations at every turn, which can reduce environmental impact.
Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing is turning traditional manufacturing economics upside down as it progresses far beyond prototyping.
Advanced CNC machining can transform your production capabilities. Combine multi-axis machining with on-machine verification to reduce setup times, minimize rework, and produce precision parts.
Predict, validate, and optimize your products using accurate analysis for mechanical simulation, computational fluid dynamics, plastic injection molding, and manufacturing.
Broaden the use of industrial robots beyond pick-and-place operations and assembly lines—access offline programming tools to automate large-scale 3D printing and subtractive processes.
PINTO BRASIL
This metalworker for automotive and other industries has reduced lead times, improved automation, and increased the standardization and control of its smart manufacturing operations using tools like Autodesk Inventor, AutoCAD Electrical, and Vault Professional.
Photos courtesy Pinto Brasil
MOICON
With the help of Autodesk Platform Services, Moicon makes a browser-based digital twin software for improving the factory floor operations and performance of smart manufacturing facilities.
CLOVER PARK TECHNICAL COLLEGE
See how one institution enacts Education 4.0—the educational transformation corresponding to Industry 4.0—and prepares students for advanced manufacturing with hands-on training in CAD/CAM software, CNC machining, 3D printing, and more.
GENERAL MOTORS
GM’s smart manufacturing journey includes making complex EV parts with AI-assisted generative design and additive manufacturing, which can lead to lighter vehicles and a shorter supply chain.
Photo courtesy General Motors
Learn more about smart manufacturing with these helpful resources from Autodesk.
A wealth of information in podcast, video, and ebook forms teaches you how a digital transformation can make a manufacturing business faster and less wasteful while also costing less.
Find out how artificial intelligence (AI) can benefit nearly every aspect of design and manufacturing, including fabrication, maintenance, quality control, efficiency, factory layout, and more.
A detailed infographic explains why a successful smart factory transformation starts with convincing managers and executives how automating repetitive processes will reduce errors that lead to injuries and waste and optimize resource use and product quality.
An Autodesk VP sheds light on how the company continues accelerating digitization and cloud connectivity on the factory floor.
Learn about the impact of smart manufacturing on business and sustainability, as well as the top 10 Industry 4.0 technologies that are making the future—and manufacturing—smart.
This comprehensive breakdown with an explainer video outlines the phases and benefits of creating a digital factory, including examples of companies that have built successful digital smart factories.
Learn more about smart manufacturing software with these top questions users frequently ask.
Several key factors differentiate smart manufacturing from traditional manufacturing. First, smart manufacturing incorporates Industry 4.0 advanced technologies such as robotics, cloud computing and mobile apps, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) sensors, and artificial intelligence (AI). Those technologies enable another differentiator: constant data collection and insight-rich data analysis from machine learning AI. Because this technology connects all parts of the production process, everyone involved can communicate and collaborate more effectively, in contrast to the more siloed operations of traditional manufacturing.
Smart manufacturing is flexible and adaptable, such as predictive maintenance that can reduce downtime. The resulting efficiencies make smart manufacturing more sustainable.
The initial steps to transition toward smart manufacturing include getting the managers and executives on board with the change. Next, define your smart manufacturing objectives, such as efficiency, flexibility, product quality, and reducing waste, and assess which of your current processes could be improved with Industry 4.0 technologies.
Before investing in technology, develop a detailed plan, including a timeline and milestones. Smart manufacturing should allow people to make the most of their positions, so factory staff will need thorough reskilling for the new processes, which other Industry 4.0 technologies like virtual and augmented reality (VR and AR) can help you do.
Data is utilized to the fullest in smart manufacturing, as data collection and analysis are two of the hallmarks of the practice. Smart manufacturing collects constant data from factory machines, sensors, and supply chain systems, while AI-powered cloud computing analyzes the data in real-time. That enables valuable insights that help decision-makers adjust systems for productivity, quality, and efficiency/sustainability improvements.
Just as importantly, data analysis also informs autonomous actions from the connected factory, where self-optimizing systems based on machine learning can automatically adjust.
A smart factory is a highly digitized shop floor that utilizes data from product design, control, fabrication, services, maintenance, and the work organization to continuously collect and share information through connected machines, devices, and production systems. AI/machine learning goes hand-in-hand with smart factory data analysis, as it can process data and recognize patterns in the data much faster than people, which helps improve efficiencies in smart manufacturing.
Connected manufacturing features networked robots and machines that can self-diagnose and warn of possible failures on the shop floor. The proliferating IIoT brings more powerful devices and machines with smart sensors that upload continuous streams of usage data to the cloud for analysis. A connected design and manufacturing process links formerly disparate operations to reveal hidden value.
Smart manufacturing helps manufacturers become more efficient, stay ahead of the competitive curve, and explore new business models and practices. Smart manufacturing also helps business efficiency by enhancing worker safety and facilitating worker training. As smart manufacturing automation captures more data points, manufacturers gain more insights into what’s happening on the shop floor, giving them a better chance to uncover bottlenecks and increase productivity.
“Smart manufacturing” is often also referred to as “advanced manufacturing” and “manufacturing 4.0.”
Meanwhile, “Industry 4.0” refers to a broader digital transformation (which smart manufacturing is a part of) where businesses can innovate faster with new business models and more tailored customer experiences based on ever-changing market conditions.