& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
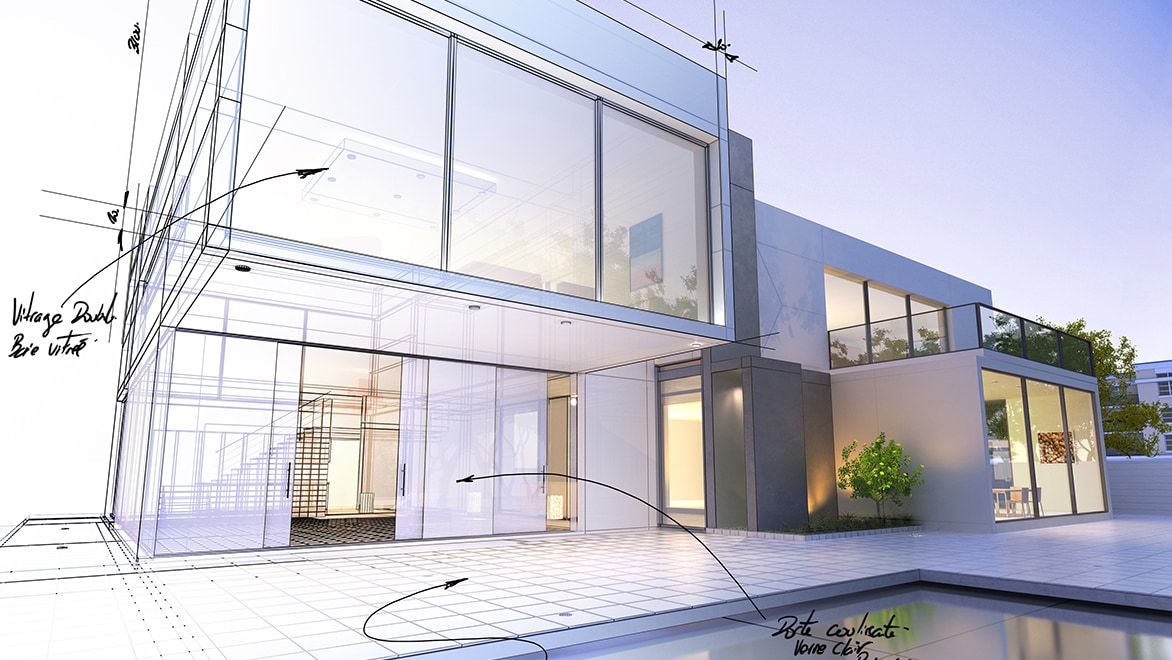
An architectural drawing is a technical illustration of a building or building project. Architectural drawings are used by architects for several purposes: to develop a design idea into a coherent proposal, to communicate ideas and concepts, to enable construction by a building contractor or to make a record of a building that already exists.
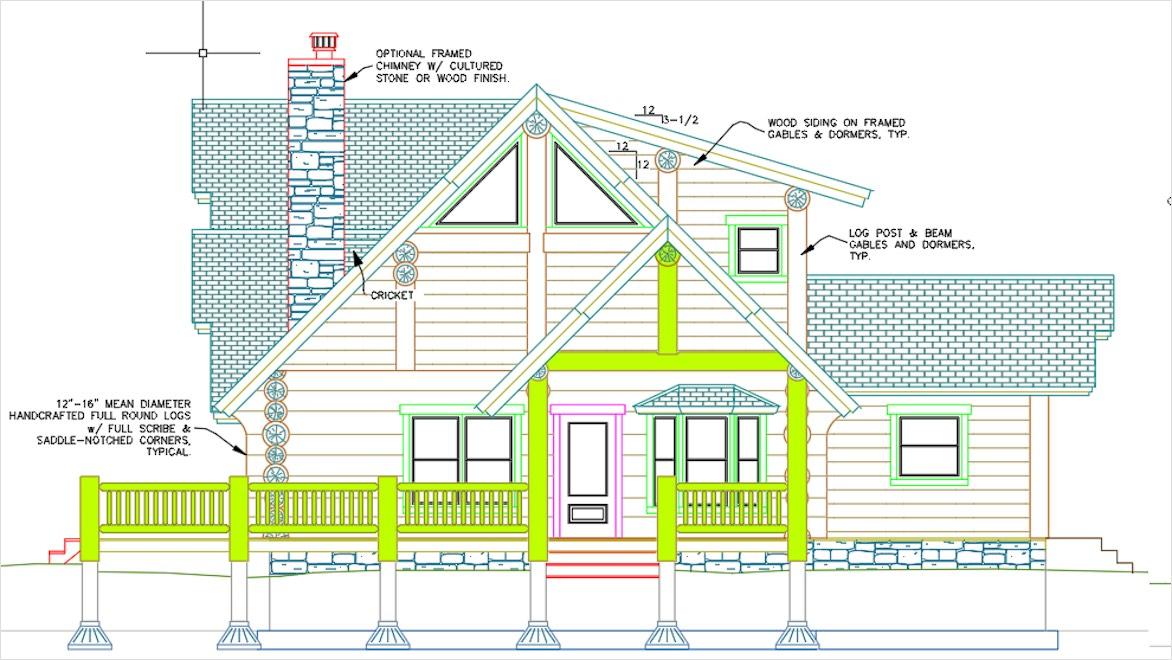
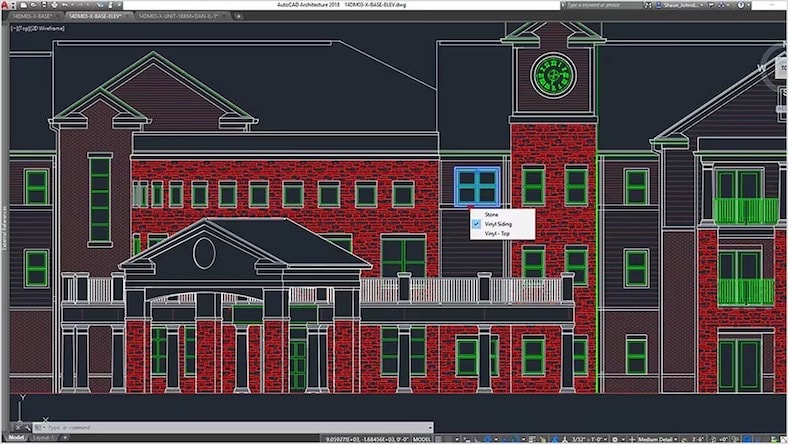
Elevations and sections are standard architectural drawings that provide essential information about a design proposal. Elevations are 2D orthographic projections of a building’s exterior façade drawn as if you’re standing directly in front of it and looking straight on. Sections are 2D orthographic representations that cut through a building to reveal its internal configuration, showing spatial relationships between floors, walls, roofs, structural framing and other elements.
Design software programmes used for architectural drawings, such as Autodesk AutoCAD and Autodesk Revit, enhance the creation of these drawings by enabling precise digital drafting, real-time adjustments, and seamless coordination. The dynamic capabilities of these tools help streamline the workflow, ensuring more accuracy and coherence between 3D models and 2D representations. Software used for architectural drawings commonly feeds into rendering and visualisation outputs so architects can present their designs convincingly. This seamless integration can improve accuracy and coordination during multi-disciplinary design reviews with structural and MEP engineers and consultants.
Architectural drawing software is commonly referred to as CAD (computer-aided design) software. Architects use this software to produce the technical drawing of a building containing specifications that are used by a contractor to construct the final architectural building. Before the existence of CAD tools and applications, architects manually drew these plans.
The process of BIM supports the creation of intelligent data that can be used throughout the lifecycle of a building or infrastructure project.
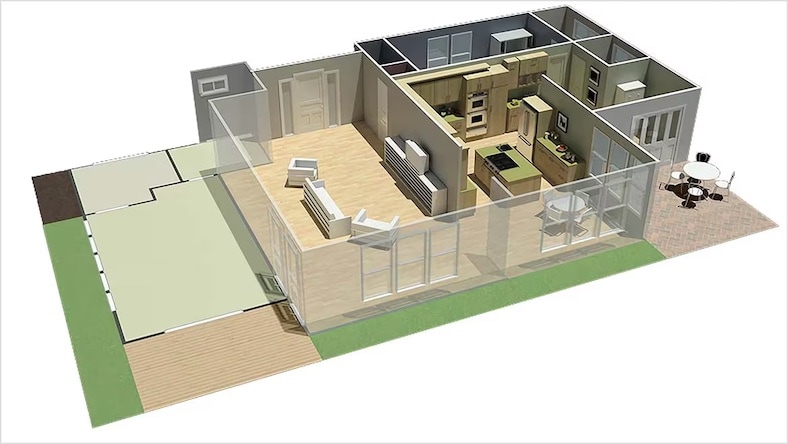
Concept drawings are used by architects and interior designers as a quick and simple way of exploring initial ideas for designs. These architectural design drawings play a key role in the early stages of the architectural design process.
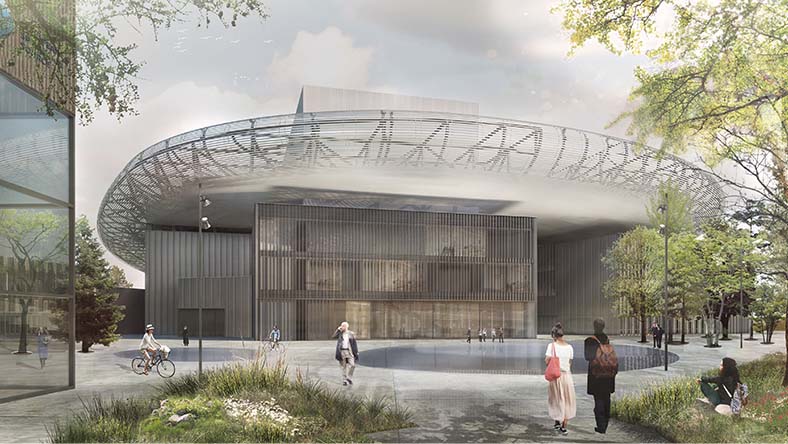
Image courtesy of CCDI Group
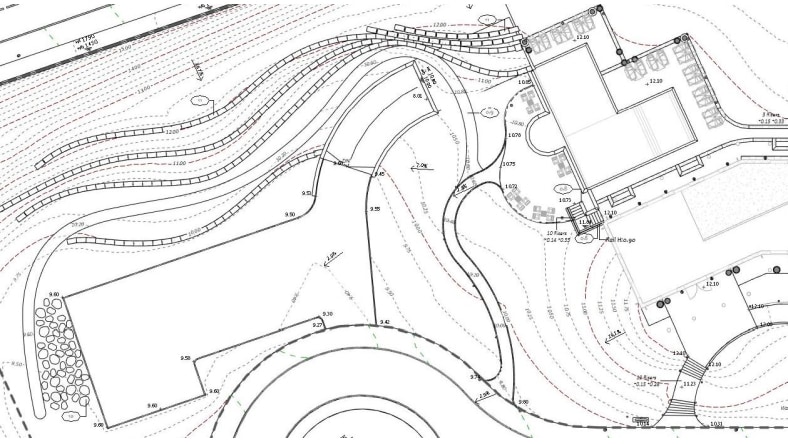
A site plan is a detailed engineering drawing that shows information about grading, landscaping, building arrangement, topography (US site) and other details. These are made easier with software that allows such information to be rapidly added.
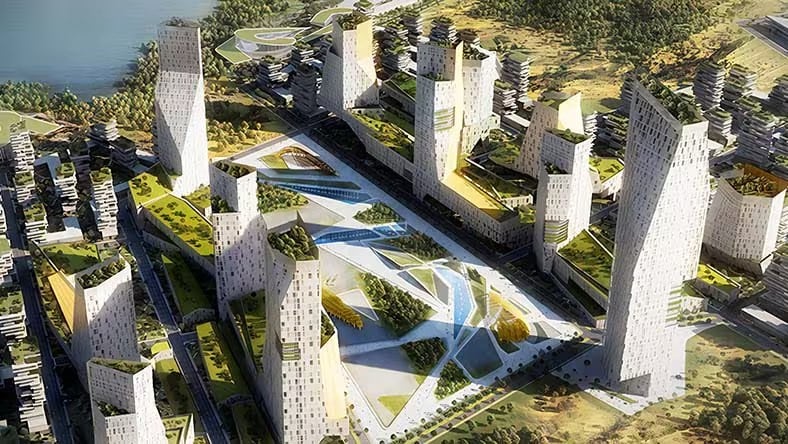
Image courtesy of Arch-Intelligence
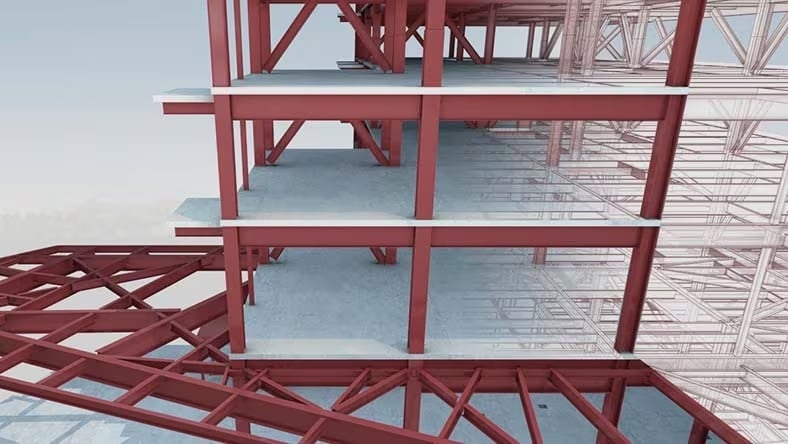
A structural drawing is a plan for how a building will be built. These architectural drawings are a crucial part of the construction documentation, and they convey how a building will be built structurally.
Image courtesy of Odeh Engineers, Inc.
Discover top architectural drawing tools and features available with Autodesk software.
Many applications support 2D drawings (like floor plans, elevations and sections) and 3D models. Intuitive drafting tools enable precise representation of spatial and structural design intent in 2D and are typically capable of developing intent into detailed construction documents (CDs). Smooth integration between 2D and 3D functionalities enhances efficiency, consistency and accuracy throughout the architectural design process.
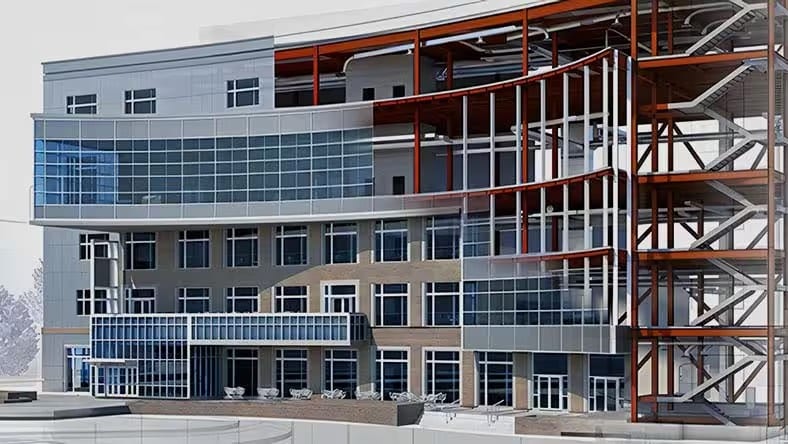
Building information modelling (BIM) (US site) improves traditional architectural drawing methods by incorporating extensive information about a building’s materials, properties and specifications into a 3D model, creating a more comprehensive digital representation. Design software with BIM capabilities helps architects develop a rich, data-driven model to visualise the design and serve as a dynamic database of information for improving coordination and collaboration among project teams.
CAD software offers precision drafting tools for creating meticulously detailed architectural drawings with unparalleled accuracy. With these advanced tools, architects can craft detailed floor plans, elevations and sections, ensuring that every dimension is precisely represented. The software’s capabilities include tools for tagging and annotation, which let users add detailed notes and specifications directly onto the drawings.
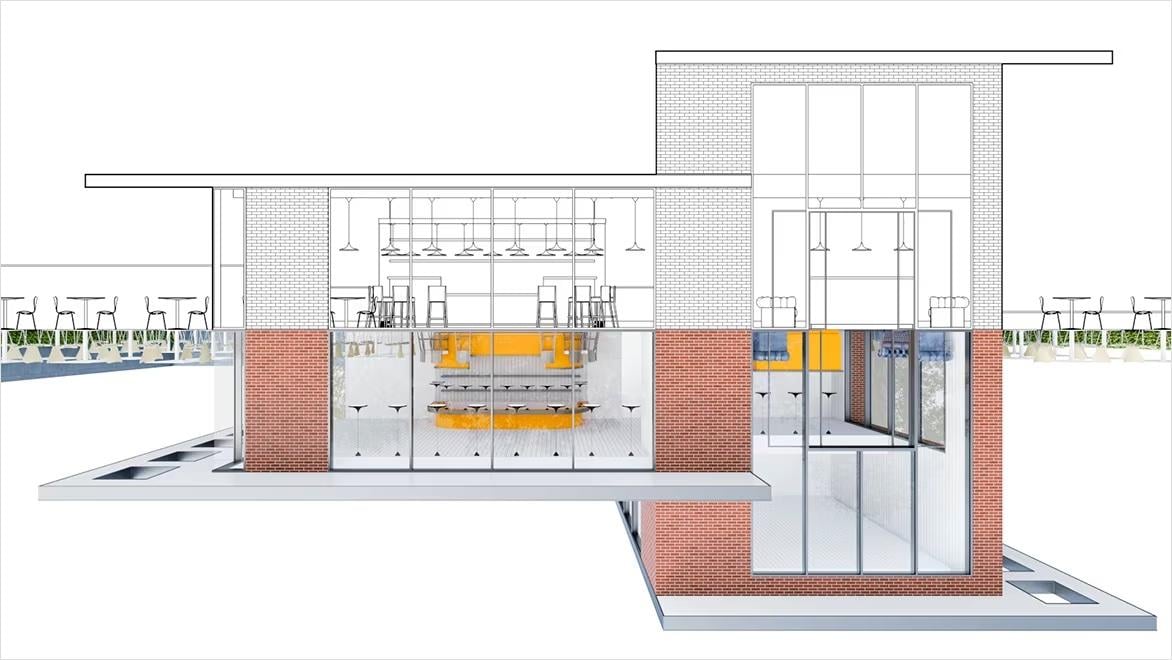
Architectural design software with advanced rendering tools lets users transform 3D models into photorealistic images or detailed animations. These tools enhance visualisations by incorporating textures, lighting and shading to simulate real-world conditions, like time of day, seasonality and location. These tools help create a more accurate preview of the final built environment, which can be used for compelling presentations, client communication and assessing environmental impacts (US site) and site orientation.
Powerful BIM and CAD tools for designers, engineers and contractors, including Revit, AutoCAD, Civil 3D, Autodesk Forma and more.
Plan, design, construct and manage buildings with powerful tools for Building Information Modelling.
2D and 3D CAD tools, with enhanced insights, AI-automations and collaboration features. Subscription includes AutoCAD on desktop, web, mobile and seven specialised toolsets.
Navisworks Manage, Navisworks Simulate software and the Navisworks Freedom 3D viewer for 5D analysis, design simulation and project review.
Best-in-class tool for 2D CAD drafting, drawing and documentation. Subscription includes AutoCAD LT on desktop, web and mobile.
Learn more about communicating architectural design intent and improving design quality using Autodesk architecture software.
Autodesk architecture software solutions support the rapid innovation needed to meet today’s design challenges.
Help clients visualise your designs with realistic renders.
Software from Autodesk empowers you to visualise, design, render and build.
Discover how our customers are using Autodesk architectural rendering software in their projects.
BORGA
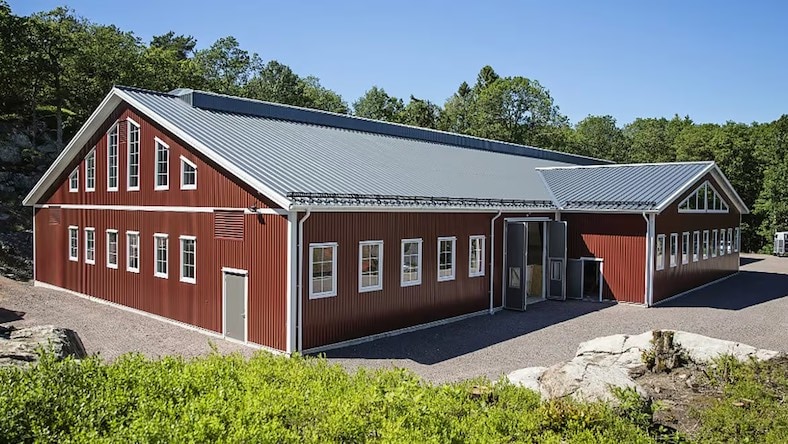
Swedish construction company Borga relies on the AutoCAD Architecture toolset or end-to-end control in the building process.
Image courtesy of Borga
STUDIO A ARCHITECTURE
See how Studio A Architecture is using AutoCAD and the Architecture toolset to create a comprehensive and luxurious senior living community in Lexington, Kentucky.
Image courtesy of Studio A Architecture
TOULOUKIAN TOULOUKIAN
Boston-based Touloukian Touloukian Inc. is revitalising downtown Detroit’s Beacon Park with AutoCAD and the Architecture toolset.
Image © Anton Grassl Photography
Learn more about design software for architectural drawings with these helpful resources from Autodesk.
Unleash your imagination, foster collaboration and boost confidence in your designs with Autodesk architecture software.
Explore essential Autodesk Revit tools for architectural drawing, focusing on setting up levels, grids and views to transition into 3D design seamlessly.
Explore how AI is reshaping architectural drawing by automating image generation, schematic design, urban planning and interior layout.
Streamline your architectural drawing workflow. Enhance project clarity, visualise design options and foster team transparency with BIM.
Embrace the future of architectural drawing with Autodesk Certification. Unlock your potential in building design through industry-validated courses.
Unlock collaborative and innovative building design solutions with BIM. Incorporate architectural design software to achieve project goals.
Many architects use Autodesk AutoCAD as a 2D architectural drawing tool for creating floor plans, elevations and sections. This architectural software speeds up the drawing process with pre-built objects like walls, doors and windows.
Used worldwide by both commercial and residential architects, CAD has replaced manual drafting. It helps users create architectural drawings and designs in either 2D or 3D so they can visualise the construction. CAD enables the development, modification and optimisation of the architectural design process.
Architects design buildings using software focused more on exteriors, while interior designers focus on the inside spaces of buildings, and include furniture, fixtures and other accessories to create a desired look and function.
BIM and CAD serve distinct and sometimes complementary purposes in the architecture and construction industry. BIM workflows typically rely on a 3D model which serves as the central data repository for design intent. This model incorporates detailed data about building components and their relationships, facilitating collaboration and supporting the entire building lifecycle. BIM emphasises information-rich, parametric modelling within a common data environment that supports interoperability and keeps all project stakeholders on the same page.
In contrast, CAD is centred around drafting workflows, focusing primarily on geometric representation. CAD lacks the comprehensive data aspect inherent to BIM and may require more manual updates to ensure the accuracy of project documentation.
Many types of architectural drawings are required during the process of designing, developing and constructing a building. Some are used at specific times and stages, and others (such as floor and site plans) are continuously evolving and being adapted as the project develops.
Software programs that produce architectural drawings enhance collaboration by offering real-time editing, cloud-based access and version control features. These tools enable multiple stakeholders to work concurrently on the same project, ensuring access to the latest versions and reducing errors. Cloud-based (US site) capabilities facilitate remote collaboration, while markup and commenting tools streamline communication. Integration with collaboration platforms (US site) and project management tools centralises project information, promoting seamless coordination between disciplines.
Most architectural drawing programs support importing and exporting drawings from and to other software applications using various file formats. Standard formats include DWG and DXF for 2D and 3D drawings, IFC for BIM data exchange in an open file format, STL for 3D printing, FBX or OBJ for visualisation, PDF for document sharing, SVG for vector graphics and STEP for 3D model data. These capabilities facilitate interoperability and collaboration between design and construction disciplines, helping architects, engineers and other stakeholders to seamlessly exchange and work on drawings and project data authored in various software applications.
Architectural drawings are detailed documents that communicate crucial information about the design and construction of a building. They typically include: